Jürgen Cito (PI)
Associate ProfessorEmail: juergen.cito@tuwien.ac.at
Google Scholar | GitHub | Twitter
Probabilistic programming provides an intuitive means to specify Bayesian models as programs and to automatically perform posterior inference with general-purpose algorithms.
This makes probabilistic modelling more accessible to non-experts in Bayesian statictics, however, it comes with new challenges.
Through the lens of software engineering, we explore new approaches to improve the probabilistic programming experience.
Derives a novel factorisation of the program density from a static analysis that approximates the dependencies between variables. Presents a compilation method based on the factorisation that speeds-up MCMC and SMC algorithms and reduces variance of a gradient estimator in variational inference.
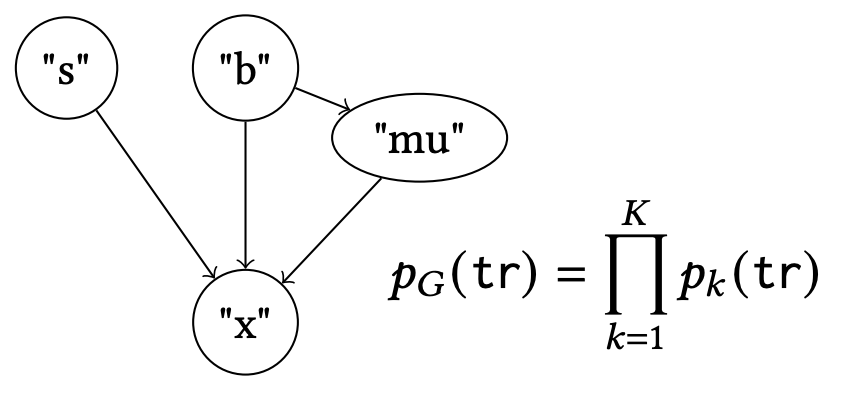
It is commonly known that any Bayesian network can be implemented as a probabilistic program, but the reverse direction is not so clear. In this work, we address the open question to what extent a probabilistic program with user-labelled sample statements and while loops - features found in languages like Gen, Turing, and Pyro - can be represented graphically. To this end, we extend existing operational semantics to support these language features. By translating a program to its control-flow graph, we define a sound static analysis that approximates the dependency structure of the random variables in the program. As a result, we obtain a static factorisation of the implicitly defined program density, which is equivalent to the known Bayesian network factorisation for programs without loops and constant labels, but constitutes a novel graphical representation for programs that define an unbounded number of random variables via loops or dynamic labels. We further develop a sound program slicing technique to leverage this structure to statically enable three well-known optimisations for the considered program class: we reduce the variance of gradient estimates in variational inference and we speed up both single-site Metropolis Hastings and sequential Monte Carlo. These optimisations are proven correct and empirically shown to match or outperform existing techniques.
@misc{boeck2025staticfactorisation,
title={Static Factorisation of Probabilistic Programs With User-Labelled Sample Statements and While Loops},
author={Markus Böck and Jürgen Cito},
year={2025},
eprint={2508.20922},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.PL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.20922},
}
Introduces a new approach for debugging probabilistic programs, where diagnostic tools evaluate the quality of inference during execution. We implemented a debugger as a VSCode extension and showed that our approach significantly reduces time and difficulty on inference debugging tasks in a user-study.
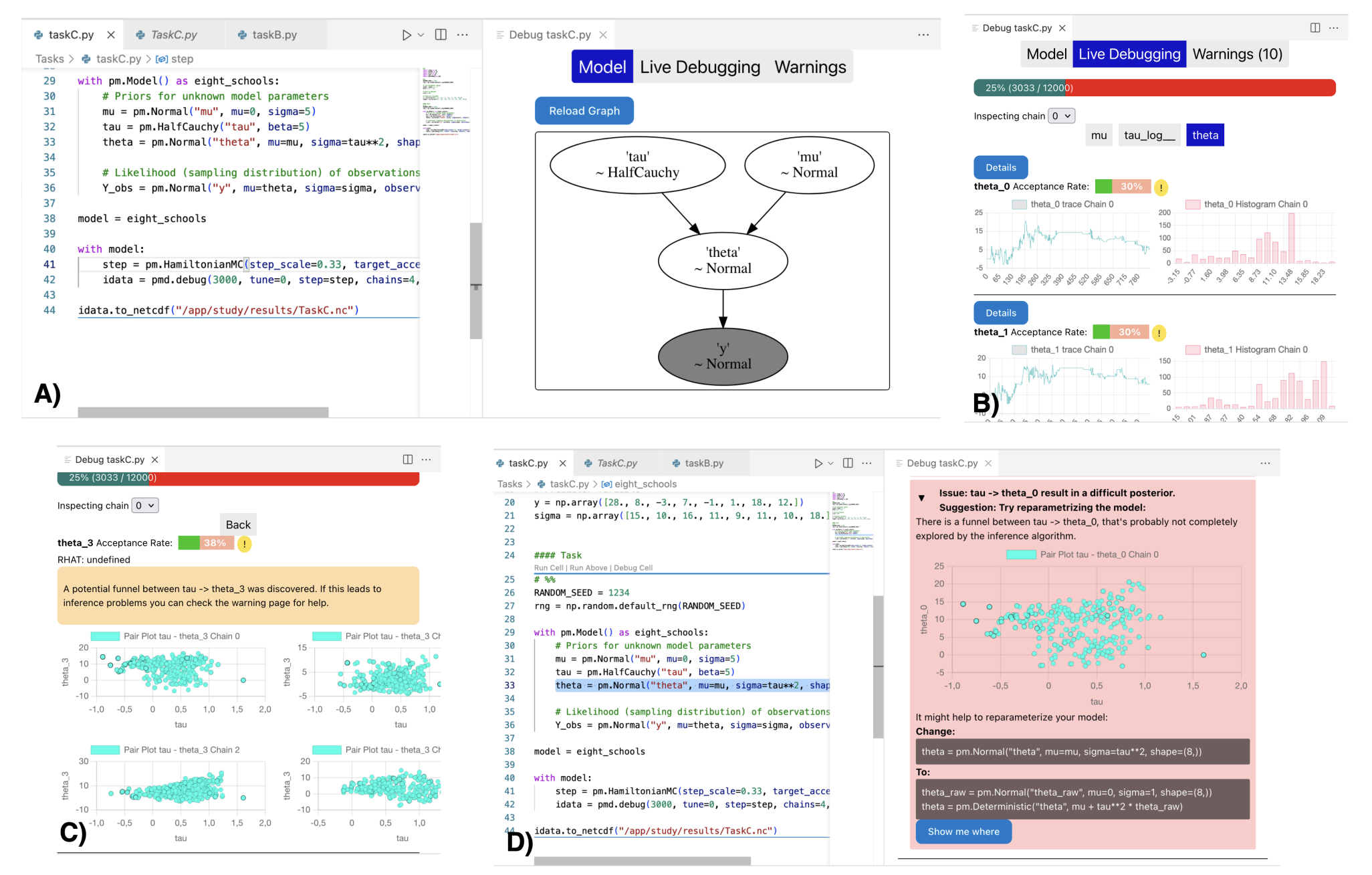
Probabilistic programming is a rapidly developing programming paradigm which enables the formulation of Bayesian models as programs and the automation of posterior inference. It facilitates the development of models and conducting Bayesian inference, which makes these techniques available to practitioners from multiple fields. Nevertheless, probabilistic programming is notoriously difficult as identifying and repairing issues with inference requires a lot of time and deep knowledge. Through this work, we introduce a novel approach to debugging Bayesian inference that reduces time and required knowledge significantly. We discuss several requirements a Bayesian inference debugging framework has to fulfill, and propose a new tool that meets these key requirements directly within the development environment. We evaluate our results in a study with 18 experienced participants and show that our approach to online and interactive debugging of Bayesian inference significantly reduces time and difficulty on inference debugging tasks.
@misc{nussbaumer2025onlineinteractivebayesianinference,
title={Online and Interactive Bayesian Inference Debugging},
author={Nathanael Nussbaumer and Markus Böck and Jürgen Cito},
year={2025},
eprint={2510.26579},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.SE},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.26579},
}
Describes a framework which allows the formulation of program analyses which target problems specific to the probabilistic programming environment in a high-level API. The analyses can be applied to any probabilistic programming language for which light-weight bindings are implemented.
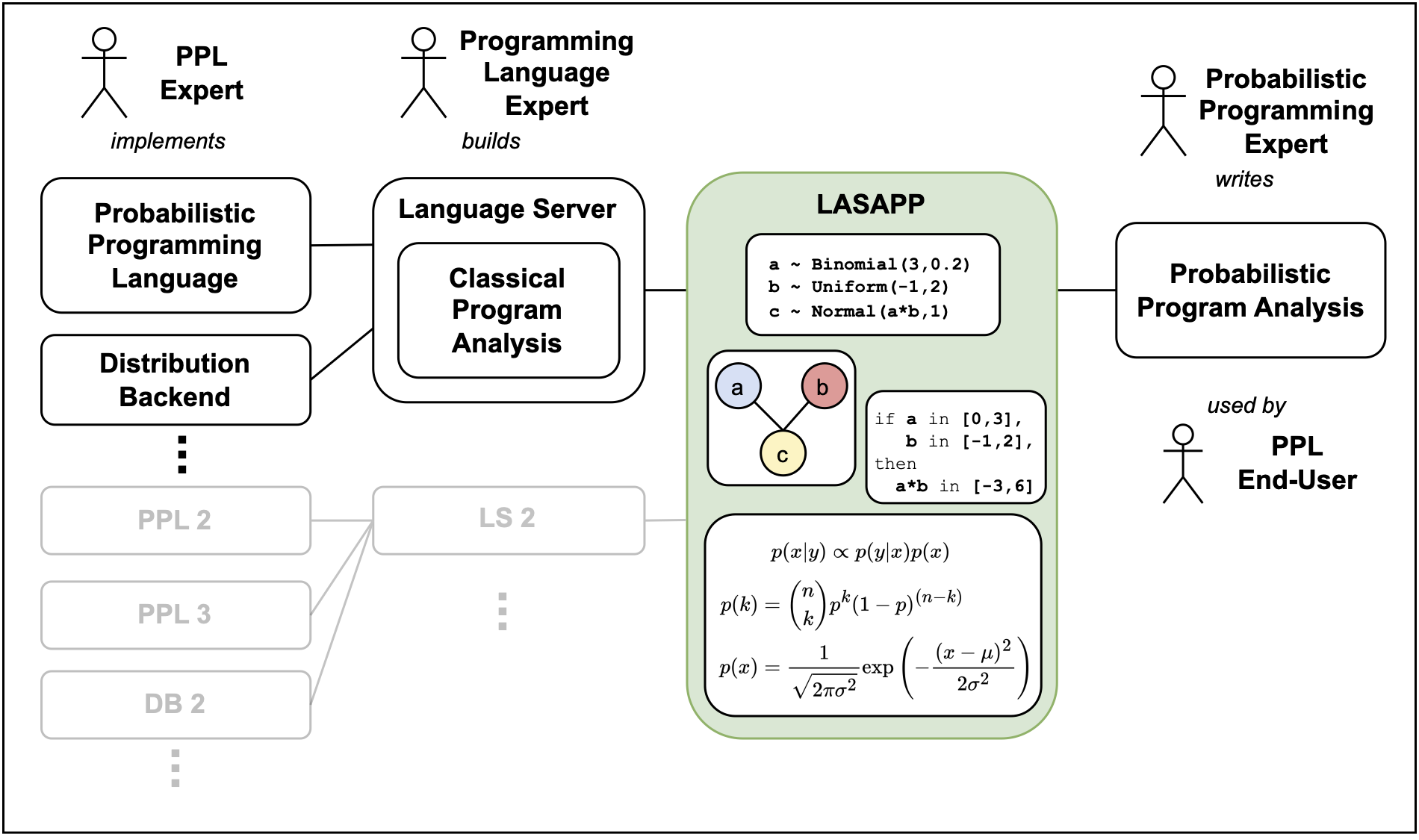
Probabilistic programming allows developers to focus on the modeling aspect in the Bayesian workflow by abstracting away the posterior inference machinery. In practice, however, programming errors specific to the probabilistic environment are hard to fix without deep knowledge of the underlying systems. Like in classical software engineering, static program analysis methods could be employed to catch many of these errors. In this work, we present the first framework to formulate static analyses for probabilistic programs in a language-agnostic manner: LASAPP. While prior work focused on specific languages, all analyses written with our framework can be readily applied to new languages by adding easy-to-implement API bindings. Our prototype supports five popular probabilistic programming languages out-of-the-box. We demonstrate the effectiveness and expressiveness of the LASAPP framework by presenting four provably-correct language-agnostic probabilistic program analyses that address problems discussed in the literature and evaluate them on over 200 real-world programs.
@inproceedings{boeck2024language-agnostic,
title={Language-Agnostic Static Analysis of Probabilistic Programs},
author={B{\"o}ck, Markus and Schr{\"o}der, Michael and Cito, J{\"u}rgen},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 39th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering},
pages={78--90},
year={2024}
}